KLHL24 mutation drives intermediate filament degradation, mitochondrial dysfunction and fibrosis in heart failure patients
Cardiovascular Research
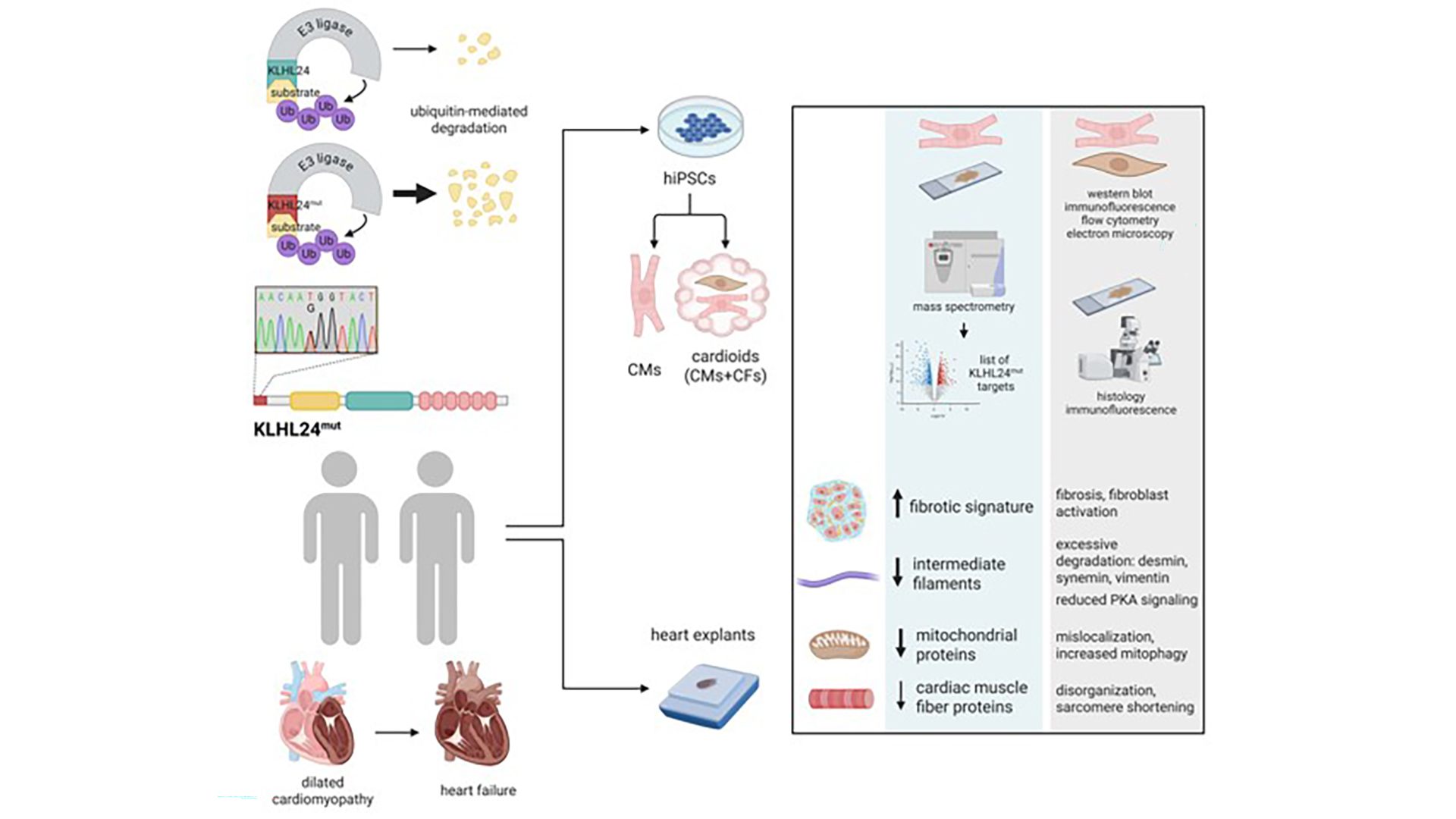
In patients with epidermolysis bullosa caused by variants in KLHL24 (KLHL24mut), dilated cardiomyopathy is often the major clinical- and life-threatening problem. In this study, Ramovs et al. employed human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) derived cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts to show that KLHL24mut causes excessive proteasome-dependent degradation of intermediate filament and mitochondrial proteins, disrupting cytoskeletal integrity, mitochondrial positioning, and sarcomere function, reproducing findings in explanted human hearts. To read why iPSC-derived cell systems are relevant for disease modeling and therapeutic target identification, read the full study.