Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors: cardiotoxicity profile and management
Inhibition of the non-receptor TK, Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK), which plays an important role in abnormal B-cell proliferation, is now the standard treatment of B-cell haematological malignancies such as chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), Waldenström macroglobulinaemia (WM), and marginal zone lymphomas (MZL).
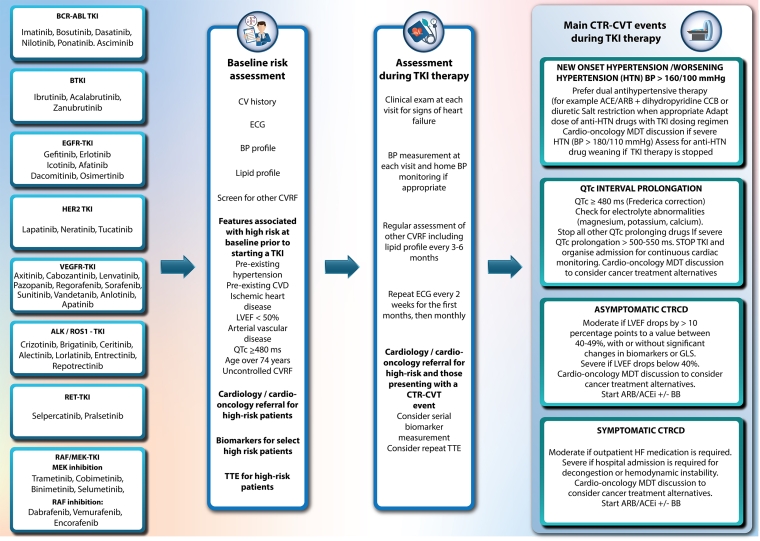
BTKI-induced CTR-CVT, baseline stratification and cardiac monitoring during treatment are summarised in Figure 1.
Ibrutinib, a first-generation irreversible BTKI, is associated with a range of CV toxicities which emerged in the original trials. Of note, BTK inhibitors are also associated with an increased risk of bleeding through platelet dysfunction which is problematic in patients requiring dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), surgery and a challenge for patients with BTKI-induced atrial fibrillation (AF), where anticoagulation is also indicated [11].
Third-generation reversible BTK inhibitors such as pirtobrutinib and nemtabrutinib, which were designed to overcome resistance to traditional BTK inhibitors through mutations whilst providing more selective inhibition with less off-target effects, are currently being assessed in phase II clinical trials.
Epidermal growth factor receptor – tyrosine kinase inhibitors: cardiotoxicity profile and management
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which is also known as HER1, is an RTK that is mutated in a subtype of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) called EGFR-mutant NSCLC and is thus inhibited by selective EGFR-TKIs. The first-generation EGFR-TKIs, which include gefitinib, erlotinib, and icotinib, are reversible. They are used in the advanced NSCLC setting as well as in the adjuvant setting. Second-generation EGFR-TKIs, including afatinib and dacomitinib, offer irreversible inhibition of the HER oncoprotein family and are generally superior to the first-generation EGFR-TKIs in the treatment of advanced NSCLC but are associated with increased toxicities. Third-generation EGFR-TKIs include osimertinib which was initially designed to overcome resistance to first- and second-generation EGFR-TKI, driven by additional mutation in the mutant EGFR (T790M). Osimertinib has now been shown to be superior to older-generation EGFR-TKIs in EGFR mutant NSCLC, especially in cases of metastasis to the central nervous system, due to its ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Other third-generation EGFR-TKIs such as almonertinib, furmonertinib, lazertinib, and nazartinib have shown promising results in phase I and II trials. Fourth-generation EGFR-TKI’s are also currently being designed to combat osimertinib resistance [3].
EGFR-TKI induced CTR-CVT, baseline stratification and cardiac monitoring during treatment are summarised in Figure 1.
Human Epidermal growth factor receptor 2 – tyrosine kinase inhibitors : cardiotoxicity profile and management
Mutations in the Human Epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) oncoprotein, which shares a similar structure to EGFR, play a crucial role in the abnormal intracellular signal transduction cascade responsible for oncogenesis and proliferation in the subgroup of breast cancers named HER2-positive (HER2+) breast cancer. Unfortunately, the ERBB2 receptor also plays a key role in cardiomyocyte damage repair, and hence its inhibition is associated with cardiac toxicity [12]. The monoclonal antibody trastuzumab is the standard treatment of HER2+ breast cancer. For more advanced disease, combination treatment with pertuzumab, or trastuzumab-drug conjugates e.g., trastuzumab-emtansine and trastuzumab-deruxtecan, are used. However, in selected patients, the use of HER2-TKIs is recommended, in particular for patients with intracranial metastatic disease, as small-molecule TKIs cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively than trastuzumab.
HER2-TKI induced CTR-CVT, baseline stratification and cardiac monitoring during treatment are summarised in Figure 1.
Lapatinib was the first reversible HER2-TKI approved in the metastatic breast cancer (MBC) setting after failure or resistance to monoclonal antibody HER2-targeting therapies such as trastuzumab [13].
As most algorithms for HER2-positive MBC include several lines of therapy, often based on combination therapies of HER2-TKIs, either with trastuzumab in its standard form or conjugated with chemotherapy, there is an increased risk of CTRCD.
Newer irreversible HER2-TKIs such as neratinib, pyrotinib and tucatinib have since then been introduced and are associated with a similar CTR-CVT profile [14].
Vascular endothelial growth factor multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: cardiotoxicity profile and management
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signalling pathway plays an important role in several cancers and the inhibition achieved by VEGF receptor-associated multi-targeted TKIs (VEGF-TKI) has become a key component of anticancer therapies against malignancies such as renal, lung, thyroid, and hepatocellular carcinomas [3].
VEGF-TKI induced CTR-CVT, baseline stratification and cardiac monitoring during treatment are summarised in Figure 1.
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase and ROS proto-oncogene 1 inhibitors: cardiotoxicity profile and management
Echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 and anaplastic lymphocyte kinase (EML4-ALK) is a fusion gene mutation that occurs in 3–5% of NSCLC. Inhibition of ALK-mutant NSCLC by ALK-TKIs has shown significant improvement in survival outcomes [3]. Several ALK-TKIs have also been used to treat ROS-1 mutant cancers including colorectal and cholangiocarcinoma. ALK-TKIs have a range of CTR-CVT.
Crizotinib is a first-generation ALK-TKI which is associated with a range of CTR-CVT outlined in the 2022 ESC Guidelines document and summarised in Figure 1. Baseline risk evaluation and cardiac monitoring during ALK-TKI therapy are also described.
Second-generation TKIs that are characterised by a higher selectivity and central nervous system (CNS) penetration include ceritinib, alectinib and brigatinib. Lorlatinib is a third-generation ALK-TKI designed to overcome acquired resistance due to secondary ALK mutations while on first- or second-generation ALK-TKIs and has a similar CV toxicity profile to crizotinib.
Rearranged during transfection - tyrosine kinase inhibitor: cardiotoxicity profile and management
Abnormal mutations in the rearranged during transfection (RET) tyrosine kinase receptor play an important role in the abnormal signal transduction pathways that lead to cancer growth. RET-TKI are therefore used in patients with RET-altered cancers such as RET fusion-positive NSCLC and RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancers [3]. Selpercatinib is a first-in-class agent that obtained FDA approval in 2020 for RET fusion-positive NSCLC and thyroid cancer based on the LIBRETTO-001 trial [15]. In this pivotal clinical trial, hypertension was the most frequently reported adverse effect in patients treated with selpercatinib.
RET-TKI induced CTR-CVT, baseline stratification and cardiac monitoring during treatment are summarised in Figure 1.
Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma and mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibitors: cardiotoxicity profile and management
Abnormal signal transduction through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway—RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK—is implicated in one-third of all malignancies, especially rat sarcoma virus (RAS) and rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (RAF) mutations. For example, the BRAF V600 mutation is found in a significant proportion of melanomas, metastatic colorectal cancer, and lung adenocarcinoma [3].
Although the mutation of MEK, also called mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), is not frequently identified in solid tumours, it is heavily involved in the downstream RAS and RAF signalling cascade and upstream of ERK. This is the rationale for combination therapies with MEK and BRAF inhibition, which are typically used in malignancies such as melanoma, NSCLC and neurofibromas.
RAF/MEK-TKI-induced CTR-CVT, baseline stratification and cardiac monitoring during treatment are summarised in Figure 1.
Other TKIs
Fibroblast growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (FGFR-TKI) have indications in metastatic urothelial cancer, and locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. Although most approved FGFR-TKIs belong to multi-targeted TKIs, more specific FGFR-TKIs such as erdafitinib and pemigatinib are also available.
Platelet-derived growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibition (PDGF-TKI) is achieved by most VEGFR-associated multikinase inhibitors and play an important role in the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST; e.g., sunitinib, regorafenib, avapritinib and ripretinib).
Dysregulation of the KIT proto-oncogene plays a central role in some malignancies such as leukaemia, GIST, and melanoma. KIT inhibition (KIT-TKI) is usually present in multitargeted TKIs such as imatinib, sunitinib, regorafenib, avapritinib and ripretinib.
Oncogenic activation of tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) is involved in several solid tumours harbouring these gene fusions. Larotrectinib and entrectinib are two approved first-generation Tropomyosin receptor kinase inhibitor (TRK-TKI) that target this abnormal oncoprotein [3].
Conclusion and Impact on Daily Practice statement
The success of targeted cancer treatments such as TKIs highlights a trend toward personalised and individualised cancer management. Cardio-oncology management in the setting of TKI therapy should aim at maximising cancer treatment outcomes whilst mitigating the adverse cardiovascular toxicity through careful baseline risk stratification and individualised cardiac surveillance during and after the cancer treatment.