Image classification and segmentation
Automation of image analysis can save time and increase accuracy, reproducibility, and standardisation, allowing early detection of cardiac disease and more accurate diagnoses and treatment planning. This can also be applicable to risk stratification and outcome prediction, leading to better patient care [4].
Machine learning algorithms use traditional methods or DL to classify cardiac images. Imaging classification through identification of cardiac views is the first crucial step in image analysis. Algorithms discover patterns, characteristics and specific anatomical landmarks in an image that may be unique to a certain label. This includes the identification of specific cardiac views (e.g., distinguishing a 2-chamber from a 4-chamber view) or more disease-specific structural/functional cardiac abnormalities (e.g., distinguishing hypertrophic cardiomyopathy [HCM] from other forms of left ventricular [LV] hypertrophy) [3]. Multiscale deep reinforcement learning has been used to precise anatomical landmark localisation. This approach has been tested on 5,000 three-dimensional (3D) computed tomography (CT) volumes, efficiently identifying landmarks in less than a second with high accuracy [5,6]. Some models may learn and become more accurate in the future, using AI to classify observed items into predetermined classes.
Following imaging classification, the next step is cardiac segmentation, which enables accurate quantification of basic parameters such as ventricular or atrial volumes, myocardial mass, or ejection fraction, by delineating anatomical structures (in 2D or 3D representations). Recent developments include DL methods combined with level sets for LV segmentation in cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) images, and temporal tracking algorithms for myocardial motion assessment across frames (allowing the assessment of function along specific axes, such as longitudinal function) [7]. More complex interpretations are also feasible, such as myocardial perfusion assessment, quantification of late gadolinium enhancement or assessment of the severity of coronary artery stenosis.
AI in transthoracic echocardiography
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is a critical modality for evaluating cardiac structure and function. Nevertheless, operator-dependent discrepancies can impact the precision of TTE assessments. Artificial intelligence has emerged as a transformative tool in this domain, enabling the uniformisation of procedures, markedly reducing this interoperator (and intraoperator) variability. These technologies now support comprehensive automated analysis for TTE interpretation, encompassing view identification, image segmentation, structural and functional quantification, and disease detection, thereby elevating the standard and reliability of cardiac assessments.
Artificial intelligence is already in place in several echocardiography laboratories. For every TTE performed there are AI algorithms that can enhance image quality by reducing noise and artifact. An example of this is harmonic image, which aids in better visualisation of cardiac structures. There are also validated AI algorithms that automatically calculate fundamental parameters such as ventricular volumes, wall thickness, ejection fraction, speckle tracking and strain analysis, offering important insights into myocardial disease (Figure 1) [8].
Figure 1. Example of heart model (in this example, from a Philips® EPIQ 7 ultrasound machine), an echocardiogram model available for quick and accurate calculation of left ventricle and left atrial volume and function.
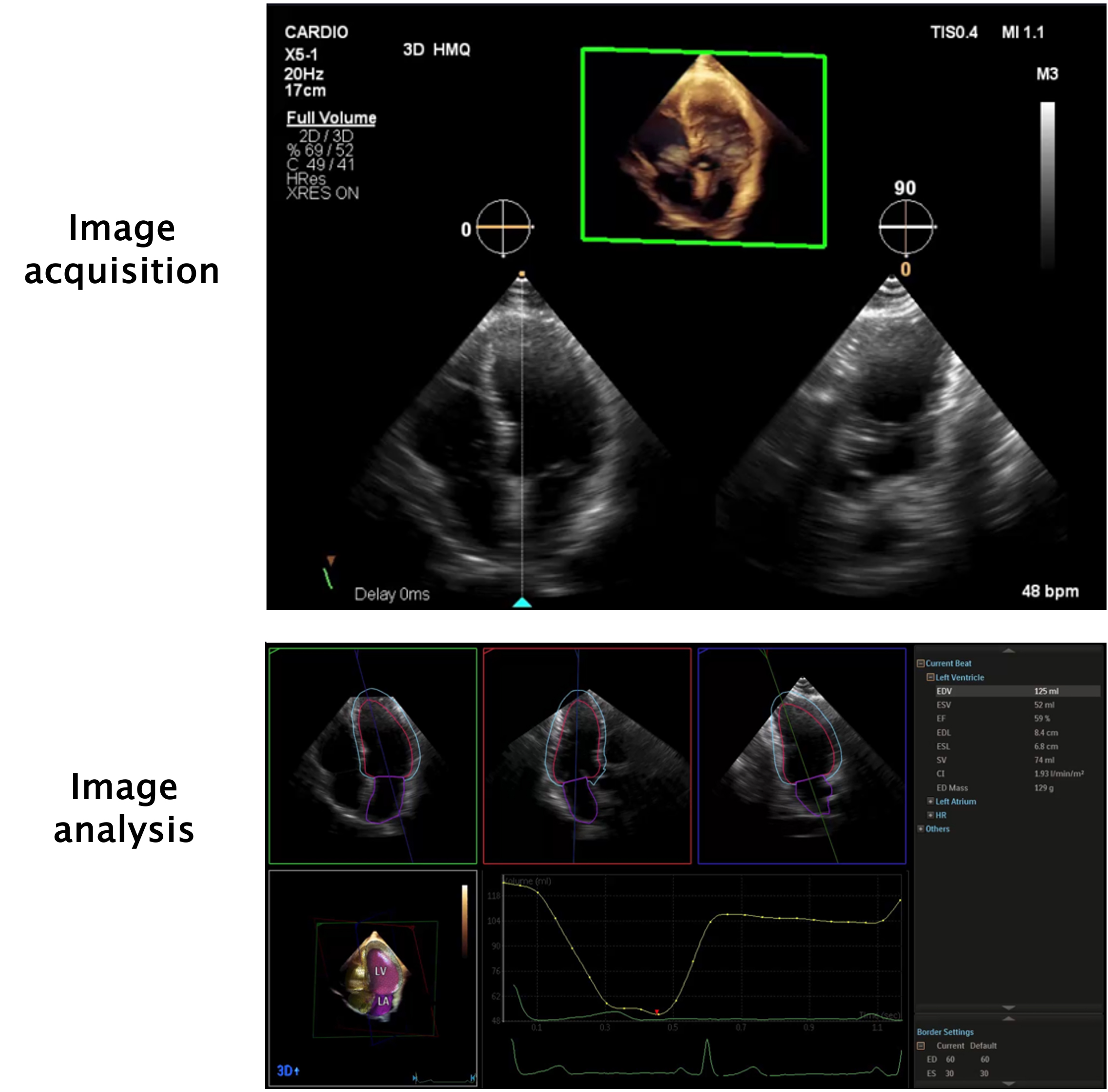
Image acquisition is shown in the top panel. A single loop from an apical 4-chamber view is necessary for the calculation of the parameters. During acquisition, the machine automatically shows a simultaneous 90º view of the 2-chamber view. In the bottom panel, from this single loop, the machine shows the apical 4-chamber, 2-chamber and 3-chamber views. A 3D model of the heart is also shown, alongside a left ventricle volume graph for each frame during the cardiac cycle. Then, in a few seconds, it calculates left ventricle and atrial volumes with high accuracy, allowing estimation of ejection fraction, stroke volume and cardiac index, as is shown on the right side of the image.
Future applications of AI in TTE are vast. Automated tools can identify several cardiac pathologies, from myocardial infarction to valvular diseases. In one study, a support vector machine was the most accurate in determining the severity of mitral regurgitation [9] and in another study ML closely matched human measurements of aortic stenosis severity [10]. Artificial intelligence can also help in the management of heart failure, identifying high-risk phenotypes who may benefit from more careful follow-up or targeted heart failure therapies, with impact in outcome and mortality [11]. The right algorithms can help us differentiate between a healthy and a diseased heart in scenarios where doubt is common; for example, differentiating between HCM and athletes’ heart [12], or between restrictive cardiomyopathy and constrictive pericarditis [13] or even differentiating myocardial infarction from takotsubo syndrome [14]. Machine learning can be of use in subjective clinical scenarios, such as detecting wall motion abnormalities, with evidence showing that it is equivalent to trained echocardiographers and superior to trainees [15,16].
Further advances not only improve the diagnostic process but can impact the management of cardiac disease, for example, using algorithms to predict survival through TTE parameters with better accuracy than clinical scores [17]. Finally, large echocardiography databases can be (re)analysed and used in clinical research, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of cardiovascular diseases.
AI in cardiac computed tomography
The application of ML methods, particularly DL, has revolutionised the diagnostic and prognostic capabilities in the field of cardiac computed tomography (CT). Due to the risk of image deterioration and motion artefacts in CT, the use of DL algorithms has enabled cleaner processing of acquired images. Numerous studies in this area have shown that image processing using AI tools allows for higher image quality, providing a level of accuracy in coronary artery disease detection that is very similar to that obtained by invasive stratification [18].
The use of ML algorithms for identifying coronary artery calcium scores (CACS) has reported very promising results, with a strong correlation with measurements made by human experts [19]. Beyond CACS determination, the application of AI algorithms has evolved into the detection and quantitative assessment of coronary lesions, with validation in real-life studies. Deep learning algorithms have also been developed to detect high-risk lesions, enabling evaluation of atherosclerotic burden, calcification, plaque thickness and severity of stenosis [20]. More recently, the advent of functional assessment of coronary lesions (CT-FFR) has prompted various studies using ML algorithms, with promising results in this area [21]. Machine learning has also been applied to epicardial fat evaluation, pertaining not only the detection and quantification of epicardial adipose tissue, but also the potential prognostic implications [18].
Finally, the applicability of these algorithms has also shown interesting results regarding risk stratification in patients with coronary artery disease, with stronger correlations with adverse outcomes, compared with more traditional scores and methods [18].
AI in cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging
Artificial intelligence techniques are revolutionising cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging by enhancing acquisition (plane automation, enhancement of image quality, reduction of scanning time), preprocessing (image normalisation and elimination of artefacts) and post-processing (automated classification, segmentation, and feature extraction) stages.
Deep learning has been instrumental in overcoming traditional CMR challenges, such as lengthy acquisition times required by its high-resolution demands. Techniques like undersampling, which involve acquiring less data and estimating the remainder, alongside ML algorithms trained on extensive datasets, have significantly accelerated CMR scan times [22]. Generative adversarial networks, for instance, enable synthesis of cine-like CMR images from real-time sequences, benefiting patients who struggle with breath-holding or who have arrhythmias, thereby improving image quality [23]. Moreover, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can tackle complex tasks such as detecting motion artefacts or misorientations early in image analysis [24].
Despite advancements, manual extraction of imaging data remains time-consuming and prone to errors, affecting fields such as cardio-oncology or heart failure management (e.g., when to decide stopping chemotherapy or implant an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator based on ejection fraction). Automated ML analysis offers a solution by promising quicker, more precise, and standardised evaluations, essential for consistent cardiac function assessment and multicentre studies (Figure 2). A study by Bhuva and colleagues showed the ability of ML to match the precision of human readers (both senior and junior doctors) in measuring LV mass, volumes, and function but at a significantly faster rate (186 times faster) [25]. More recently, in another study, ML assessed cardiac structure and function from CMR images, aiming for greater precision than human analysis. Trained on a diverse dataset, the algorithm demonstrated superior precision and speed compared to humans, notably enabling a reduction in the sample size needed in trials using LV ejection fraction as an endpoint [26]. A specific population of HCM patients who underwent scan-rescan (two scans each) CMR showed that ML measures maximum wall thickness with superior precision and lower variability than 11 CMR experts. This suggests the potential of ML in enhancing diagnosis and risk stratification in HCM [27].
Figure 2. AI-segmentation of a CMR scan in a patient with Fabry disease (in this example, using 1CMR software, Mycardium AI Precision Cardiac Diagnostics, Liverpool, UK).
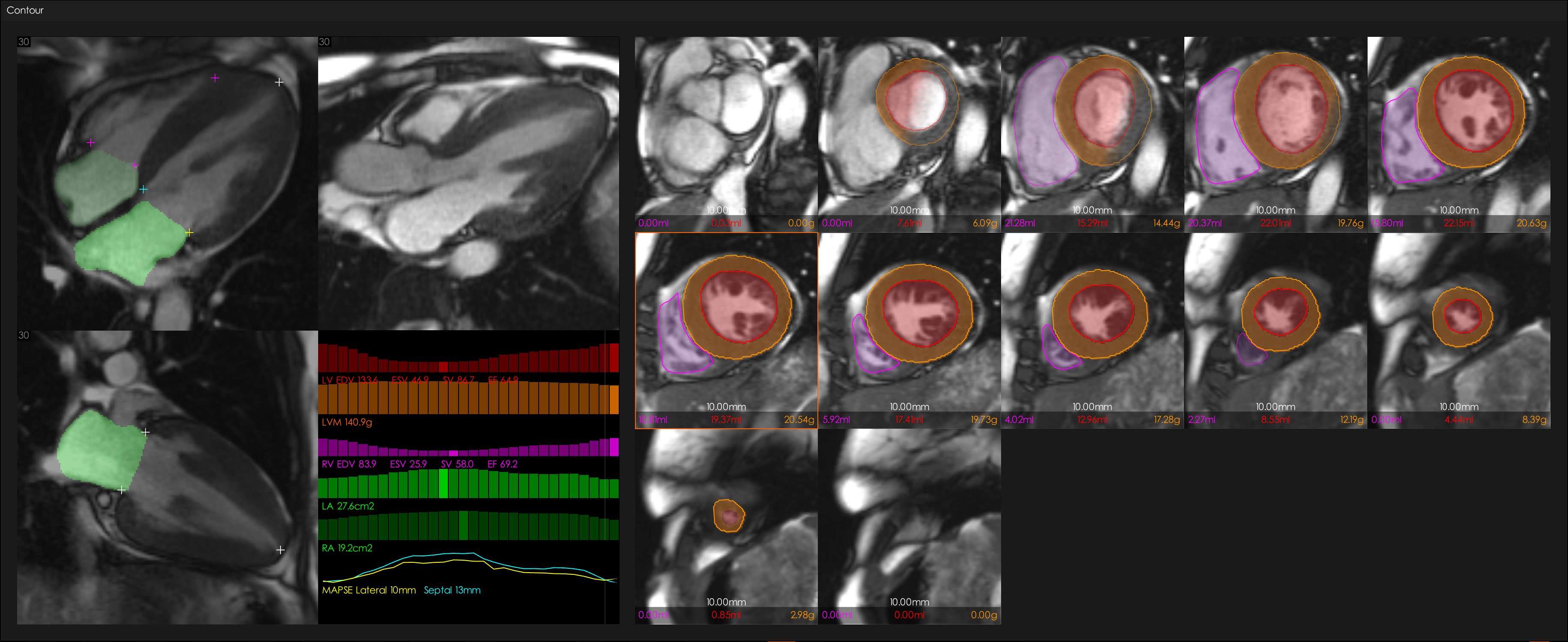
In the left panel, 4-chamber, 2-chamber and 3-chamber views are shown, with markers indicating the tricuspid and mitral valve insertion points, and the apex of the right (RV) and left (LV) ventricles. A graph is shown below with ventricular volumes, mass, mitral annulus plane systolic excursion (MAPSE) in the lateral and septal points, and atrial areas through the cardiac cycle. In the right panel, the LV short axis cine stack is shown with the AI-derived LV and RV contours (image courtesy of James Moon and Rhodri Davies).
AI in the catheterisation laboratory
AI-based tools have emerged to automate the analysis of imaging modalities utilised in the catheterisation laboratory, aiming to streamline these techniques and enhance cardiovascular diagnosis and treatment.
Starting with coronary angiography, numerous studies have demonstrated the feasibility of recognising angiographic patterns and characterising lesions using DL-based models. For example, Du and colleagues showed a precision rate of 76.9%, 75.1%, 74.2% and 79.0% for the detection of diameter of stenosis, calcification, thrombus, and dissection, respectively [2,28]. Regarding intracoronary imaging, AI applications to optical coherence tomography (OCT) and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) have focused on image segmentation (e.g., lumen area and plaque burden), plaque analysis (e.g., calcium identification), and stent assessment (e.g., expansion and apposition) showing excellent agreement with analysis by experts [2,29].
The functional assessment of coronary stenosis is now possible by means of AI-guided wire-free algorithms. These virtual fractional flow reserve (FFR) systems are based on angiography and computational fluid dynamics (Figure 3) and demonstrate excellent correlation with invasive FFR [2,28,29]. Moreover, novel computational methods based on OCT and IVUS allow morpho-functional assessment within one single imaging pullback, achieving excellent diagnostic accuracy to identify significant FFR [28].
Figure 3. Example of quantitative flow ratio (QFR, Medis, Leiden, the Netherlands and Pulse Medical Imaging, China), one of the virtual FFR systems commercially available, showing the functional assessment of the left anterior descending artery.

QFR: 0.77 corresponds to a haemodynamically significant lesion (cutoff value <0.80).
AI-based software has also been designed to improve navigation and guidance during both coronary and structural heart disease interventions. The Dynamic Coronary RoadmapTM (Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands) overlays coronary arteries onto fluoroscopic images in real-time, facilitating continuous visual feedback during intervention and resulting in reductions in contrast volume and fluoroscopy time [28]. Similarly, technologies like TrueFusionTM (Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) and EchoNavigatorTM (Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands) work by integrating the fluoroscopy with transoesophageal echocardiography, enabling better communication between echocardiographers and interventionists, thus enhancing anatomical orientation during structural procedures [2,28,29]. Other major applications of AI in interventional cardiology are outside the scope of this article and include prognostic predictive models and robotics.
Conclusions and future perspectives
In summary, AI in cardiovascular imaging is a growing field with considerable potential to aid in diagnosis and serve as a powerful tool for prognosis, thanks to its ability to process large amounts of data. However, it is important to approach the use of AI with caution, considering these algorithms as supplements to, rather than replacements for, the expertise of medical professionals. As we look ahead, the prospects for integrating AI in patient care are encouraging, suggesting that the future of this technology is already taking shape.
Patient-oriented messages
When discussing the use of AI in cardiovascular imaging with patients, doctors should aim to explain the purpose, benefits, and limitations of AI technologies in a clear and accessible manner. It is important to convey that AI can enhance the precision, efficiency, and also the personalisation of diagnostic processes by aiding in the detection, characterisation, and prognostication of cardiovascular diseases. They should reassure patients that AI tools are used to support, not replace, the expert judgement of healthcare professionals, ensuring an added layer of precision to their care. Additionally, doctors should address any privacy concerns by explaining how patient data is protected and used responsibly within these technologies.





















