PFO closure in CS
PFO closure methods and limitations
Data from randomised trials and a meta-analysis support PFO closure in high-risk patients. These recommendations are based on the probability of the role of PFO when other aetiologies of CS have been excluded. Many RCTs, such as the CLOSE [19], REDUCE [20], DEFENSE-PFO [21] and the RESPECT [11] with prolonged follow-up, have shown that in patients <60 years with a high-risk PFO, closure in the first 6 months after the index stroke reduces stroke recurrence but not mortality.
In several metanalysis, despite methodological limitations, consensus exists that PFO device closure should be performed in CS patients with the highest risk. No differences have been reported about superiority of a specific device.
PFO closure may have potential complications. 6.3% subjects had recurrent stroke and/or TIA, and 3.9% subjects had a residual right-to-left shunting in a cohort of 730 patients who underwent PFO closure for CS [22]. New incidence AF varies depending upon the PFO device delivered, (13% for the Cardioform, 4% for the Helex and 4% for the Amplatzer). Moreover, rare, but devasting are device thrombosis, embolism, displacement, infective endocarditis and aortic root erosion [23]. Consequently, it is imperative that patient selection identifies those who most will benefit from the intervention.
PFO closure decision should be undertaken by a multidisciplinary team (MDT), that includes a neurologist in order to confirm that the CS is most likely due to an embolic event, that the PFO has high-risk features, to exclude causes of embolic stroke, especially AF, and to confirm anatomical eligibility for device closure and review the risk of complications. The indication should be discussed with the patient with a clear and complete explanation of the risks and benefits of the procedure, any additional medical therapy required, and any alternative options.
Medical therapy and PFO
The alternative to PFO closure is medical therapy which should be considered in low-risk patients without indications for PFO closure, and an assessment of bleeding risk versus the PFO-stroke related relapse risk should be made. Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) may be the best choice in low bleeding risk patients but requires good compliance and adequate monitoring. Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) need further study to extend their use in this setting. Whilst DOACs have shown greater antiembolic protection and a reduced bleeding risk compared to VKA in patients with AF, the results compared to antiplatelet agents in CS have not been confirmed.
Antiplatelet therapy is an alternative when the risk of stroke is low. In the RESPECT trial [11], in the medical therapy arm with anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy there was no benefit of PFO closure among the patients with indication to anticoagulation.
Patient selection for PFO closure
Patient characteristics
A young age (≤ than 60-years-old), no common cardiovascular (CV) risk factors, no other potential CV causes of thromboembolism, concomitant DVT or DVT risk factors, ASA or a large shunt association are considered as the main patient characteristics that favour a PFO closure for secondary prevention after a CS. ASA association justifies the PFO closure. There is less agreement about shunt entities without an ASA or other risk factors. However, a study meta-analysis showed a benefit in PFO closure in large shunts, also independently of ASA. The same indication is found in the CLOSE [19] and DEFENSE-PFO [21] trials in selected high-risk patients, with or without ASA.
Two risk scores have been proposed to assess the relationship between stroke and PFO. The Risk of Paradoxical Embolism (RoPE) mainly includes clinical features while the PFO-Associated Stroke Causal Likelihood (PASCAL) classification system includes both the RoPE score and the anatomical features of an ASA and large shunts (Table 1).
Table 1. RoPE Score and PASCAL Classification System.
RoPE Score: Characteristics and Points
- No history of:
- Hypertension (+1)
- Diabetes (+1)
- Stroke or transient ischaemic attack (+1)
- Non-smoker (+1)
- Cortical infarct on imaging (+1)
- Age (in years):
- 18–29: +5
- 30–39: +4
- 40–49: +3
- 50–59: +2
- 60–69: +1
- 70: 0
PASCAL Classification System
- High RoPE score (≥7) and high-risk PFO feature (large shunt and/or ASA)a:
- Both absent → Stroke unlikely related to PFO
- High-risk PFO feature present, high RoPE score absent → Stroke possibly related to PFO
- High RoPE score present, high-risk PFO feature absent → Stroke possibly related to PFO
- Both present → Stroke probably related to PFO
aA large shunt size is defined as >20 bubbles in the left atrium on TOE; ASA defined as >10 mm of excursion from midline. ASA: atrial septum aneurism; PASCAL: PFO-Associated Stroke Causal Likelihood; PFO : patent foramen ovale; RoPE: Risk of Paradoxical Embolism
Based on these combinations of factors, the original, extended PASCAL classification system assigns the likelihood of a causal relationship to five levels: definite, highly probable, probable, possible and unlikely. The PASCAL algorithm [24] was developed using a mixed methods approach, incorporating expert judgement, physiological and epidemiological data and the validated RoPE score.
What the guidelines say
Over the last ten years, a series of position papers and guidelines about PFO management have been published. In 2013-2016, US stroke guidelines tributed to PFO closure in CS a class 2b recommendation. After the 2017 publication of the CLOSE [19], REDUCE [20], and DEFENSE-PFO [21] trials and 3 metanalyses in 2018-2019 favouring PFO closure for CS, consensus statements from the French Society of Cardiology [14] and the European Society of Cardiology were published in 2019. Percutaneous PFO closure in CS patients with ASA or isolated PFO with large shunts was recommended [18]. The American Heart Association (AHA) stroke guidelines in 2019 underlined doubts about the quality of the RCTs and favoured PFO closure versus antiplatelet therapy, but not versus anticoagulant therapy [25].
In 2022, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions Guidelines recommended PFO closure in patients aged 18 to 60 years (strong recommendation, moderate certainty of evidence), suggesting that a RoPE (risk of paradoxical embolism) score ≥7 may identify patients at greater benefit [26].
Finally, in 2024 the European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Guidelines were published, developed with a strong and tight Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) methodology [27]. However, some questions remain unanswered and require larger evidence from RCTs as well as critical review and evaluation.
Management in daily clinical practice
Despite the aforementioned limitations, the ESO Guidelines [27] are now the reference for clinical practice in the field of CS management and PFO closure. The population, intervention, comparator, outcome (PICO) questions consider: the diagnostic performance of cTTE, cTCD and cTOE, the risk reduction of CS relapse after PFO closure plus antiplatelet agents versus antiplatelet alone, the use of the PASCAL classification in patients with different age classes, the management of anti-aggregation or anticoagulation in the short- or long-term as an alternative or in association with PFO closure.
The use of risk stratification tools was not prespecified in the PICO questions and therefore no systematic review was conducted with regard to the PASCAL classification system. Nevertheless, it was used because it was associated with a clear, demonstrated differential treatment effect, but was degraded by one level because it was not used as an inclusion criterion or stratification variable in any existing RCTs, nor was it prospectively validated.
The conclusions on PFO closure are [27]:
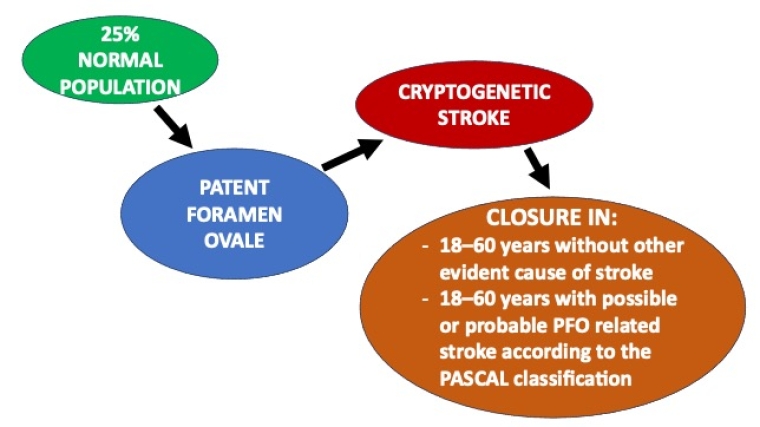
- In patients aged 18–60 years without other evident cause of stroke but a PFO, PFO closure in selected patients is recommended in addition to antiplatelet therapy (Quality of evidence: High - Strength of recommendation: Strong for intervention).
- In patients aged 18–60 years with possible or probable PFO related stroke according to the PASCAL classification, PFO closure in addition to antiplatelet therapy is recommended (Quality of evidence: Moderate - Strength of recommendation: Strong for intervention).
- In patients aged 18–60 years with unlikely PFO-related stroke according to the PASCAL classification, the suggestion is against PFO closure unless there is a high probability of clinical causality enhancing the risk of paradoxical embolism (non-cerebral embolism, deep venous thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism close to index stroke, pulmonary arterial hypertension, history of sleep apnoea or other hypoxaemic conditions associated with PFO, Valsalva at stroke onset, recent history of prolonged immobility, recent airline travel, presence of venous thrombophilia, decompressive illness in divers, platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome or a Eustachian valve or other anatomical features on echocardiography) (Quality of evidence: Low - Strength of recommendation: Weak against intervention).
- In patients older than 60 and younger than 18 years, no evidence-based recommendation can be provided (Quality of evidence: Very Low + Strength of recommendation: N/A).
- Given the lack of evidence for the timing of PFO closure, PFO closure is suggested within 6 months post index stroke, based on randomised studies. However, as secondary prevention procedures are time-dependent, PFO closure should be performed as soon as possible based on each patient’s clinical scenario, including stroke lesion size and risk profile.
About antithrombotic therapy the guidelines indications are [27]:
- In patients undergoing PFO closure, dual antiplatelet therapy is suggested followed by single antiplatelet therapy to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke, based on the protocol of available RCTs (Quality of evidence: Low - Strength of recommendation: N/A).
- No evidence-based recommendation can be formulated regarding the duration of single antiplatelet treatment (Quality of evidence: Low - Strength of recommendation: Weak against intervention).
- An individualised approach is suggested for the choice of antithrombotic therapy for patients with PFO-related stroke refusing PFO closure. Anticoagulation over antiplatelet therapy should balance PFO-related stroke recurrence risk with the long-term risk of major bleeding and consider the patient’s preference.
Indications on AF screening [27]:
- In line with the ESO guidelines on screening for AF after CS, in patients <55-year-old in PFO-associated stroke, basic cardiac monitoring for 24h by telemetry or Holter-ECG before closure is suggested.
- The use of an ILR is suggested to detect paroxysmal AF in patients with CS and PFO older than 60 years.
- When an ILR has been implanted before PFO closure, the monitoring for AF should continue until the end-of-life of the recorder.
- Systematic implantation of monitoring devices after PFO closure is not recommended.
- A systematic use of ILR when recurrent stroke after PFO closure occurred without other obvious causes for recurrence, regardless of age.
Impact on practice statement
PFO is a very frequent condition and in the absence of symptoms it should be considered as an anatomical variant instead of a pathologic condition and the patient should receive reassurance. In patients <60 years of age with a CS, the PFO should be carefully evaluated, according to its characteristics, if there is an indication for its closure, for the prevention of new cerebral episodes.
TOE is considered as the ‘gold standard’ for PFO evaluation but has some limitations. The percutaneous closure of a PFO with commonly used devices generally is a relatively easy and safe procedure, but in a certain relatively small percentage of patients’ side effects like AF are possible. As a consequence, the identification of the patients who may benefit most by this procedure imposes the need for a careful evaluation and risk stratification and is best addressed by a multidisciplinary team.